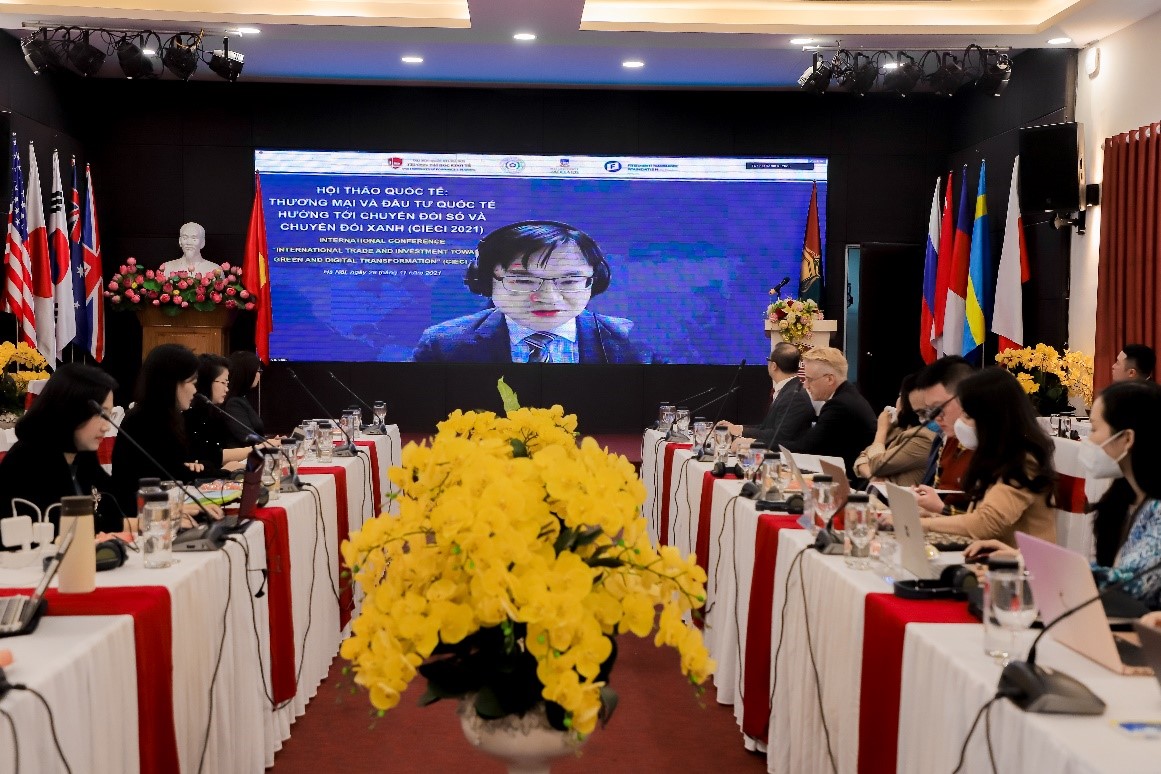
Attending the seminar, from VNU University of Economics and Business, there were Assoc.Prof.Dr. Nguyen Truc Le - Rector, Assoc.Prof.Dr. Nguyen Anh Thu - Vice-Rector. On the side of the University of Adelaide, Australia, there was Prof. Peter Draper - Dean of the Faculty of Economics and Public Policy, Director of the Institute of International Trade. On the side of National Chengchi University, Taiwan, there was the presence of Prof. Robin K. Chou - Professor Emeritus of Finance, President of Asian Finance Association, Vice Dean of Faculty of Commerce. On the FNF side, there is Prof. Andreas Stoffers - Country Manager. In addition, there were also representatives of State management agencies: Ms. Nguyen Thi Dieu Trinh, Deputy Director of the Department of Science, Education, Natural Resources and Environment, Ministry of Planning and Investment; Ms. Le Thi Ha - Head of Policy Department, Department of E-commerce and Digital Economy, Ministry of Industry and Trade. The seminar also received the attention and companionship of Assoc.Prof.Dr. Mai Quang Vinh, Chairman of the Board of Directors of Vietnam Digital Economy Cooperative Union, Director of Green Technology Institute, Green Path Vietnam Import-Export and Trading Joint Stock Company. And most of all, the conference attracted the participation of more than 200 policymakers, experts, international scholars, graduate students from government agencies, universities, and colleges.

The workshop was divided into two sections for discussion. The morning session featured presentations by representatives of organizations' scientists on the value and various aspects of developing the digital economy and greening the economy. The studies focused on the proposed implementation of the EU's carbon border adjustment mechanism, making several recommendations for businesses exporting to Europe to have a plan in place to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Parallel to the proposed emission reductions, the digital trade restriction indicators will be statistically compared in detail to guide their use in impact studies of tariff or non-tariff measures, both regionally and globally. Assoc.Prof.Dr. Nguyen Anh Thu also presented research findings on the EU's Trade Strategy's transition to a digital and green economy. The authors have made practical policy recommendations to assist Vietnam in overcoming obstacles encountered while implementing its strategy of digitization and greening the economy.
Following that, in the morning session, keynote speakers and delegates participated in a roundtable discussion titled "Greening and Digitization in International Trade and Investment: Policy Implications for Vietnam". Representatives from policy-making agencies in Vietnam, including the Ministry of Planning and Investment and the Ministry of Industry and Trade; and representatives from FNF Vietnam and Green Path Vietnam Trading and Import-Export Joint Stock Company. Experts and speakers focused on exchanging information about other countries', regions', and Vietnam's digitalization and greening policies, as well as on the experiences of businesses undergoing digital and green transformation. This discussion session shared the outcomes of the 26th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP26) as well as their implications for Vietnam.
 Prof. Robin K. Chou - Professor Emeritus of Finance, President of the Asian Finance Association, Vice Dean of the Faculty of Commerce, National Chengchi University, Taiwan presented at the conference with the theme: “Psychology CEOs and corporate cash holdings: Evidence from CEO tweets on Twitter.
Prof. Robin K. Chou - Professor Emeritus of Finance, President of the Asian Finance Association, Vice Dean of the Faculty of Commerce, National Chengchi University, Taiwan presented at the conference with the theme: “Psychology CEOs and corporate cash holdings: Evidence from CEO tweets on Twitter. On the same day, three parallel discussion sessions on the following topics were held in three conference rooms: (1) Green economy, (2) Digital economy, and (3) Sustainable development. A large number of speakers from domestic and international universities, including Australia, Poland, Russia, Taiwan, and Japan, aided in separating the morning session's topics. deeper analysis, while also contributing to the strengthening of international academic ties.
The Conference's presentations and discussions demonstrated that Vietnam is confronted with new opportunities for economic development in the direction of digital transformation and greening. The workshop produced some policy recommendations to assist Vietnam is rapidly integrating into the world's new development trend toward sustainable and modern development:
1. Implications for greening the economy
To ensure that green growth contributes to renewing the growth model, strengthening the economy's resilience, and reducing people's vulnerability to external shocks, in the coming years, solutions to several issues must be prioritized:
For Government:
- Raising awareness and energizing leaders at state management agencies, sectors, local governments, and businesses about the importance of green growth. It is critical to recognize that green growth must be approached holistically, not just as an integrated part of development decisions, but as a unified whole comprised of components of sustainable development. As a result, it is necessary to develop and implement communication and propaganda campaigns to educate the political system, businesses, and the general public about the importance of implementing green growth and contributing to the development of a developed country;
- Continue to strengthen the institutional and legal frameworks for all sectors, particularly those with a significant impact on the process of green growth;
- A strong emphasis on science and technology, as well as digital transformation, innovation, and social determinants. Create an open-ended investment incentive mechanism for green growth;
- Align domestic and international resources and strengthen international cooperation to attract foreign direct investment capital to the primary green growth sectors of clean energy, agriculture, industry, and consumption... It is critical to emphasize the importance of financial resources as leverage in particular. At the moment, the capacity for implementation is largely dependent on financial and technical assistance from international organizations and non-governmental organizations. It is critical to promote and attract additional private investment in green growth and environmental protection.
For Enterprises:
- Enterprises must clearly define their challenges and opportunities, adhere to environmental regulations, innovate technology and increase production efficiency, restructure their organizations, and restrain the growth of industries. The economy generates significant waste, contributes to pollution, degrades the environment, utilizes resources economically and efficiently, and cultivates a cadre of "green" entrepreneurs.


2. Implications for promoting digital transformation
Globally, the development of the digital economy has been an unavoidable trend. The benefits that the digital economy brings, such as increased administrative and production efficiency, competitiveness, and a narrowing of trade gaps between countries and regions, have all contributed significantly to the acceleration of economic development. national broad. Vietnam does not currently have a strategy for the digital economy, and the Ministry of Information and Communications Technology and other ministries are still developing comprehensive policies and strategies to promote the digital economy and digital transformation. Vietnam has numerous opportunities and favorable conditions for the development of the digital economy, including the fastest broadband connection in the world and a mobile network that covers the majority of the country. However, the economic application of digitization has fallen short of the potential and requirements of the changing economy. The application of information technology and people's digital transformation to economic activities remains insufficient. The business is still in its infancy. While legal documents exist, there is a general lack of sanctions and specific objectives. To help Vietnam develop its digital economy, the workshop discussed the following policy implications:
For government:
- Develop and improve institutions, laws, and policies to establish a foundation for the development of the digital economy. Establish a specialized, competent, and highly accountable institutional agency dedicated to the development of the digital economy, typically under the auspices of the government and in collaboration with relevant ministries and sectors. The state should promulgate decrees governing data sharing, electronic authentication, personal data protection, and individual privacy, as well as the resolution of disputes and conflicts arising from business, commercial, and civil activities conducted in the digital environment.
- Accelerate the reform and digitization of state management agencies and businesses, including the establishment of a national data infrastructure and the development of a strategy for digital governance. Reform administrative procedures vigorously, including simplification, digitization, electronification, and information transparency, to benefit individuals and businesses. Concentrate on e-government, e-banking, e-transactions, and e-commerce development.
- Assistance in strengthening the capacity and competitiveness of Vietnamese businesses, with a particular emphasis on cultivating, disseminating, and equipping the Vietnamese business team with the knowledge necessary to meet the requirements of the digital economy and emerging trends. Industry 4.0, as well as adapting to the new era's global market integration. There should be an incentive mechanism to encourage the adoption of digital technology by small and medium-sized businesses, as well as financial support to assist businesses in transforming digitally and promoting innovation.
- Encourage and promote the use of electronic payments throughout the economy. Utilize modern electronic payment methods such as QR code scanning and mobile e-wallet payments.
- Equip knowledge, unify thoughts and actions in the digital economy, radically altering leadership, management, and socioeconomic management thinking in the digital economy.
- Enhance the educational and training quality of human resources for the digital economy. Which places a premium on developing and attracting digital technology experts and entrepreneurs; Renovating education and training to retrain the workforce to keep pace with the advancements in digital technology; Enhance and supplementing existing training programs in schools on digital technology, digital platforms, from coding to design thinking, and the necessary digital skills for the future; Promote training and practice collaborations between universities and the business sector in the application of digital technology; Create policies that connect the domestic science and technology community to the international community, particularly the overseas Vietnamese community.
For Enterprises:
- Enterprises must also actively integrate digital technology, promoting the development of digital manufacturing and business solutions; optimizing business models and maximizing the efficiency of intelligent supply chains; and leveraging digitization to increase participation in global value chains.
- Providing staff with new technology skills, such as increasing accessibility, creative thinking, and adaptability to an ever-changing and evolving technology environment;
- Acquiring new management models, as well as production and business ideas based on new technologies, as well as fostering the emergence and development of technological innovations
3. Implications for promoting sustainable development
At the moment, all countries strive for sustainable development goals, but achieving them is difficult, particularly for developing countries. Additionally, numerous factors affect developing countries' efforts to achieve sustainable development goals, including political stability, environmental protection, and the quality of human resources. Environmental protection is one of the most critical and pressing issues facing the world today. To facilitate the implementation of the commitments made at the COP26 Conference, which Vietnam recently joined, the following policy implications are provided:
For government:
- Restructure the economy in conjunction with resource exploitation and efficient and sustainable resource use, while minimizing environmental pollution and producing low carbon emissions. Provide a roadmap for the economy's transition to low-carbon growth and circular economy development, taking environmental costs into account when investing in development;
- Increase investment and public spending in areas that promote the greening of the economy by promoting the use of new energy, renewable energy, new materials, environmentally friendly fuels, and materials;
- Advance scientific and technological research in the fields of energy, climate forecasting, early warning of natural disasters and extreme weather, resource investigation and assessment, environmental observation and monitoring, and database development on natural resources and the environment;
- Strengthening effective mechanisms for countries to cooperatively share benefits in bilateral and multilateral cooperation on resource sharing and environmental protection, such as cooperation on water and natural resource sharing, and resolving cross-border pollution problems... Actively integrating into the world, utilizing the international community's financial, technical, technological, and management support for sustainable development that is compatible with environmental protection;
- Foster the growth of new businesses with innovative products and business models that are environmentally friendly.
For Enterprises:
- Define the business's long-term goals and vision for sustainable development;
- Define sustainable development criteria that are compatible with reality and business objectives; on that basis, select the criteria that must be met during a specified period.
- Emphasis on the development and use of environmentally friendly technologies.
4. Several additional policy implications
Vietnam benefits from the fact that the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA) is a new generation free trade agreement (FTA) that shares many values with the EU's new trade strategy. EVFTA includes commitments on labor, environment, sustainable development (green), and e-commerce (digital), resulting in more breakthroughs and new opportunities for Vietnam's cooperation relationship with the EU. However, the EVFTA is a necessary but insufficient condition for promoting trade and investment relations between Vietnam and the EU, particularly now that the EU has launched a new trade strategy, which includes numerous new and broader points. for instance, the digital economy... EVFTA will be effective only if the EU moves manufacturing and supply chains from China to Vietnam to diversify and reduce its reliance on China while maintaining strategic security. Vietnam should prioritize the following issues to capitalize on this opportunity:
- Be prepared for negative consequences of the EU's new trade remedies and protectionist barriers; on the other hand, for Vietnamese goods that benefit from preferential tax rates, there must be safeguards against being exploited. a point of transshipment for goods, putting the country at risk of EU sanctions.
- Adopt EU technology, such as renewable energy, and capitalize on and expand this trend to improve national quality standards.
- Continue to improve the business environment, particularly in areas such as intellectual property or green energy, digital economy, carbon tax, subsidy transparency, technology transfer, and state-owned enterprises that do not meet developed country standards for infrastructure, human resource quality, and technological level;
*
As can be seen, the Workshop has developed into a forum for policymakers, business executives, business associations, and domestic and international researchers to exchange and share experiences on issues relating to the economic transformation toward digitization and greening. Because the global economy is currently confronted with numerous serious challenges, the policy implications for the government are critical in assisting Vietnam in implementing its digital transformation and greening strategy toward sustainable development. Simultaneously, Vietnamese businesses can use the Workshop's implications to prepare for a pandemic and develop a sustainable business strategy toward greening, following the new criteria adopted at the COP26 conference.

 Print page
Print page Back page
Back page